|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 Germany
|
|
 Light artillery
|
|
|
Contributor :
|
Location :
Israël
Avihayil
Bet Hagdudim museum
Coordinates :
Lat : 32.35180 / Long : 34.87626
|
General comments on this surviving gun :
Charlie Clelland comments : These are ex-Swiss Krupp 75mm M1902 export guns. The carriages were modified in the 1920s to permit higher elevations. The Swiss were getting rid of the Krupp guns after WW2 and Israel bought about 120 of them. The Israelis modified them for vehicle towing by using wheels from old 25 Pounder guns dumped in Italy and modifying the axles so the guns were still balanced on the smaller wheels.
A few years ago I had an email exchange with a curator of the Yad Mordecai museum in Israel. He had a complete but rather tatty 75mm gun. After many months we worked out that the Israeli 75mm guns were originally from Switzerland. The Swiss were early (1903) purchasers of the 75mm Krupp export guns, I've never found the exact number but it seems to have been around 200 guns. Initially they operated them as field guns with limbers, as was the practice at the time.
In 1922 many of the Swiss 75mm guns were modified to increase the maximum elevation by altering the rear of the trail.The top was cut off the trial and the side rails moved apart to allow the barrel to traverse at maximum elevation.
The Swiss Army removed the 75mm Krupp guns from service in 1945 and they were stored in a scrapyard pending disposal. (The Swiss also produced 75mm guns with rear mounted trunnions and fortress guns using the Krupp 75mm barrel and receiver.)
The Israelis heard of these guns and purchased about 120 in 1948. They managed to get about 50 usable guns. Although some of the Swiss guns were used by the Israelis with the original wooden wheels most were modified by
adding pneumatic tires which could be towed at much higher speeds. The wheels, it is believed, came from the vast dumps of WW2 British equipment in Italy and are wheels from 25 Pounder guns. To fit the smaller diameter wheels plates were welded to the original cut off axles and these were then welded to stub axles on the smaller wheels. The Israeli 75mm guns were used during the War of Independence and, as training guns, into the 1950s.
The Israelis had access to disarmed Sherman tanks from the Italian scrapyards and attempted to rearm the Shermans with 75mm Krupp guns. It's believed about 6 were converted but they never solved the problems with fitting tank sights to the gun.
Images are of a Swiss 1903 Krupp gun and the 1922 modification.
Identical items in the same location :
2
Items covered by this file :
1
|
|

|

|

|
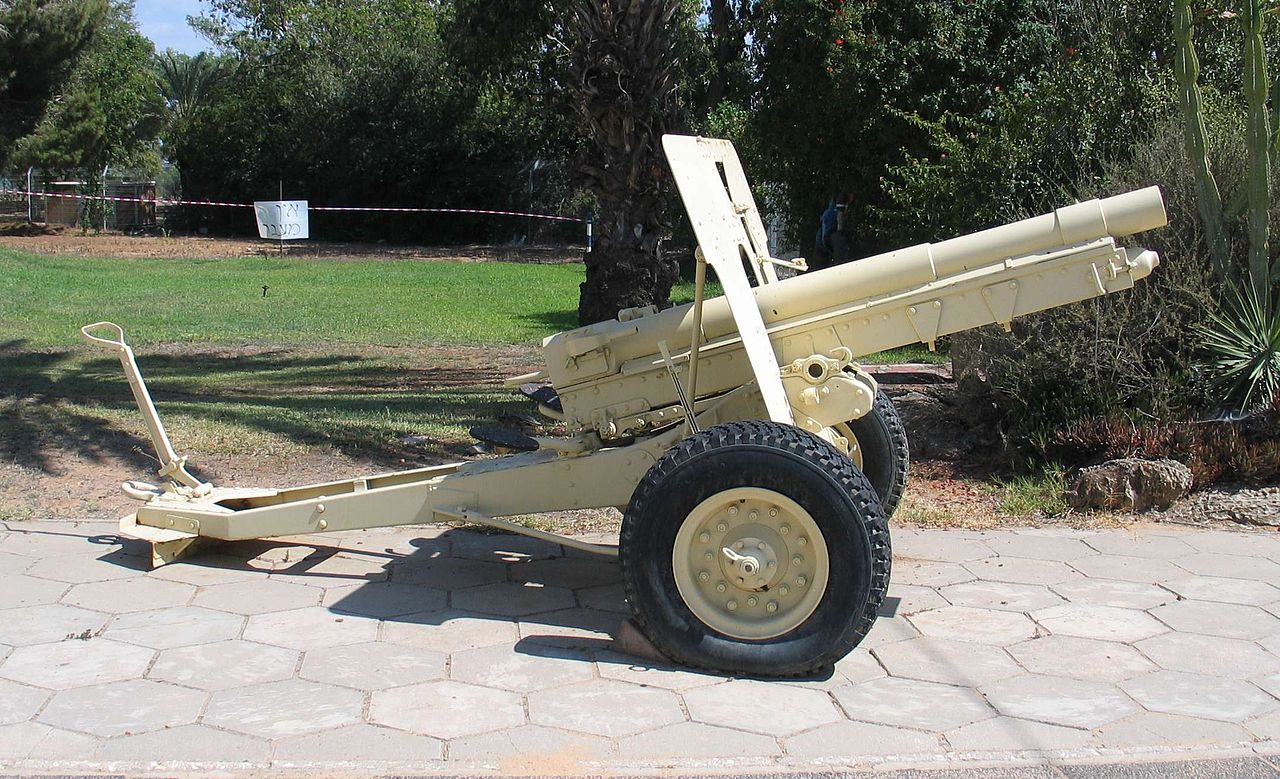
Some experts say these tubes are not coming from German 77 FK96 nA, but indeed from some Krupp export guns
|
The barrel and the recuperator have been assembled on a modern carriage
|
Markings : 'Fried Krupp AG Essen 1905 - Nr 225'
|
|
|
Historic and technical information
|
|
Denomination :
7.7cm FK 96 n/A
|
Origin :
 (
RheinMetall)
(
RheinMetall)
 (
Krupp )
(
Krupp )
|
|
Historic context :
Faced to the sudden obsolescence of its new but so conventionnal Krupp fieldgun 7.7cm FK 96 ('FK' = FeldKanone = Fieldgun) because of the appearance of the revolutionary new French 75 mle 1897 fieldgun and the demonstration of its capacities on a battlefield in China in 1900, Krupp was ordered to coordinate with its most serious competitor Rheinmetall to engage a costly modernization program that would integrate this company technical innovations.
Indeed, Rheinmetall was proposing for some years modern devices denied by the APK (Artilerie Prufungs Komission) that the Krup gun was cruelly missing : a quick-acting breech (Ehrardt-Rheinmetall) and a hydro-mechanic recoil recuperator designed by Haussner (Rheinmetall).
Ironically, this brilliant engineer could not convince its use by his employer already in 1888, when he was working for. The powerful bult conservative... Krupp (!). That new gun was genuinely named '7.7 cm FK 96 n/A' ('n/A' = neue Art - new mark) since it was - at least on the paper - only a modification of the existing gun.
However, in practice, this operation was Consequent since on the tube only, the workshops had to machine the rear chamber in order to accommodate the use of assembled ammunitions, change the whole breech, re-machine the diameter and slighrly shorten the barrel to lighten the gun, add side guides, and mount on a new recuperator. The carriage was almost a new one with a longer trail, a shield was added, ...
The few rare remaining guns that were not modernized were named '7.7 cm FK 96 a/A' ('a/A' = alte Art - ancient mark)
Manufactured since 1904 by Krupp and RheinMetall and introduced in the batteries from 1906, that fieldgun was the backbone of the light artirrely of the German army. This country entered in war in 1914 with 5068 guns of that type, organised in powerful 6 guns batteries for the field artillery and 4 guns batteries for the cavalry divisions. 3744 fieldguns 77 FK 96 n/A were still in service at the armistice.
This was a modern and efficient gun, whose perfomances are comparable to the French "75", but for the maximum range (500m lower for the German gun with the initial shell type).
A whole generation of guns derivated from that concept were commercialized by the German indusrty before the Great War for exportation in various countries. During the war, IInd Reich allies such as Turkey and Bulgaria were dotated with the same guns.
|
Technical data :
- Complete description : 77mm light fieldgun M 1896 n/A
- Design year : 1904
- Calibre : 77.00 mm
- Weight in firing position : 971 kg
- Weight for transportation : 1477 kg without the ammunition trailer, 1812 kg with it
- Tube length in calibres : 27.00 (total tube length) - 21.2 for the grooved part only
- Grooves : 32 (progressive angle)
- Projectile weight : 6.85 kg
- Initial speed : 465 m/s
- Fire rate : 12 rounds / min
- Range : 7800 m to 8300 m
- Elevation range : -13 / +15 degrees
- Direction range : 8 degrees total range
|
Sources
|
-
German Artillery of World War One Herbert Jager Crowood 2001
-
L'Artillerie de Campagne de l'Armée Impériale Allemande - Tome III - 7,7cm Feld Kanone 96 nA Bernard Delsert B.D. 2013
|
|